그래프

📍 용어
- 정점(Vertex): 그래프의 노드 또는 점
- 간선(Edge): 정점 간의 연결. 부모-자식 개념 없음
- 가중치(Weight): 간선(엣지)에 할당된 값으로, 주로 두 노드(정점) 간의 관계의 강도, 비용, 거리 등을 나타냄
- 차수(Degree): 정점에 연결된 간선의 수
- 진입 차수: 방향 그래프에서 특정 정점으로 들어오는 간선의 수
- 진출 차수: 방향 그래프에서 특정 정점에서 나가는 간선의 수
- 경로(Path): 그래프의 두 정점 간에 존재하는 간선의 연속
- 사이클(Cycle): 시작 정점에서 출발하여 다시 시작 정점으로 돌아오는 경로. 트리와 가장 큰 차이
- 연결 그래프: 모든 정점이 서로 연결된 그래프
- 포화그래프: V 개의 정점을 가지는그래프는 최대 V *(V–1)/ 2 간선이 가능
- ex) 4개 정점이 있는 그래프의 최대 간선 수는 (4*3/2) = 6개
- 부분 그래프(Subgraph): 원래 그래프의 일부 정점과 간선으로 구성된 그래프
- 방향 그래프: 간선에 방향이 있는 그래프. 예를 들어, A ➡️ B는 A에서 B로 가는 방향을 의미
- 무방향 그래프: 간선에 방향이 없는 그래프. A와 B 간의 관계는 양방향으로 해석
📍 그래프를 사용하는 예
1. 소셜 네트워크: 사람(정점)과 사람 간의 친구 관계(간선)를 나타내는 그래프
2. 도로망: 도로의 교차점(정점)과 도로(간선)를 표현하는 그래프
3. 웹 페이지: 웹 페이지(정점)와 링크(간선) 간의 관계를 나타내는 그래프

👩🏻💻 구현해보기
- 인접행렬로 저장한 그래프
/*
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000, 0 ≤ M ≤ N×(N-1)/2)
둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 간선의 양 끝점 u와 v가 주어진다. (1 ≤ u, v ≤ N, u ≠ v)
같은 간선은 한 번만 주어진다.
6 5
1 2
2 5
5 1
3 4
4 6
*/
package graph;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 인접행렬 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int[][] adjM = new int[N + 1][N + 1]; // 1부터 N까지 사용하므로
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
// 무방향 그래프의 경우 양쪽 모두에 1을 설정
adjM[u][v] = 1;
adjM[v][u] = 1;
}
// 인접 행렬 출력 (디버깅 용도)
System.out.println("인접 행렬:");
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
System.out.print(adjM[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}- 인접리스트로 저장한 그래프
/*
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000, 0 ≤ M ≤ N×(N-1)/2)
둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 간선의 양 끝점 u와 v가 주어진다. (1 ≤ u, v ≤ N, u ≠ v)
같은 간선은 한 번만 주어진다.
6 5
1 2
2 5
5 1
3 4
4 6
*/
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 인접리스트 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
List<List<Integer>> adjL = new ArrayList<>(N + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
adjL.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
// 무방향 그래프의 경우 양쪽 리스트에 추가
adjL.get(u).add(v);
adjL.get(v).add(u);
}
// 인접 리스트 출력 (디버깅 용도)
System.out.println("인접 리스트");
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": "); // 정점 번호 출력
for (int neighbor : adjL.get(i)) {
System.out.print(neighbor + " "); // 인접한 정점 출력
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}
그래프를 탐색하는 방법
1. DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)


- DFS 인접행렬 구현
/*
정점수
간선수
탐색시작노드
간선수만큼 연결정보
5
5
1
1 2
1 5
2 3
2 4
3 4
출력: 1 2 3 4 5
*/
package graph;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DFS_인접행렬탐색 {
static int[][] arr;
static boolean[] isSelected;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int V;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
arr = new int[V + 1][V + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
arr[u][v] = arr[v][u] = 1;
}
isSelected = new boolean[V + 1];
dfs(start);
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
static void dfs(int curV) {
isSelected[curV] = true;
sb.append(curV).append(" ");
for(int toV = 1; toV <= V; toV++) {
if(!isSelected[toV] && arr[curV][toV] != 0 ) {
dfs(toV);
}
}
}
}- DFS 인접리스트 구현
/*
정점수
간선수
탐색시작노드
간선수만큼 연결정보
5
5
1
1 2
1 5
2 3
2 4
3 4
출력: 1 2 3 4 5
*/
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DFS_인접리스트탐색 {
static List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] isSelected;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
list.get(u).add(v);
list.get(v).add(u);
}
isSelected = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(start);
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
static void dfs(int cur) {
isSelected[cur] = true;
sb.append(cur).append(" ");
for(int i : list.get(cur)) { // 갈 수 있는 곳들만 뽑음
if(!isSelected[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
}
}
2. BFS(너비 우선 탐색)
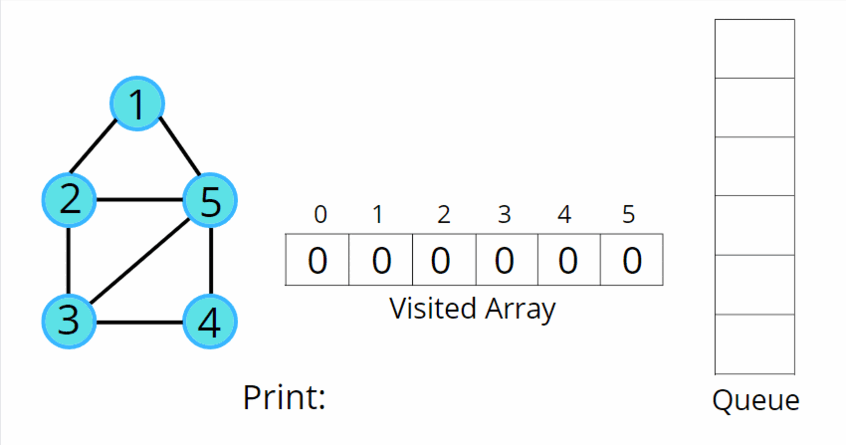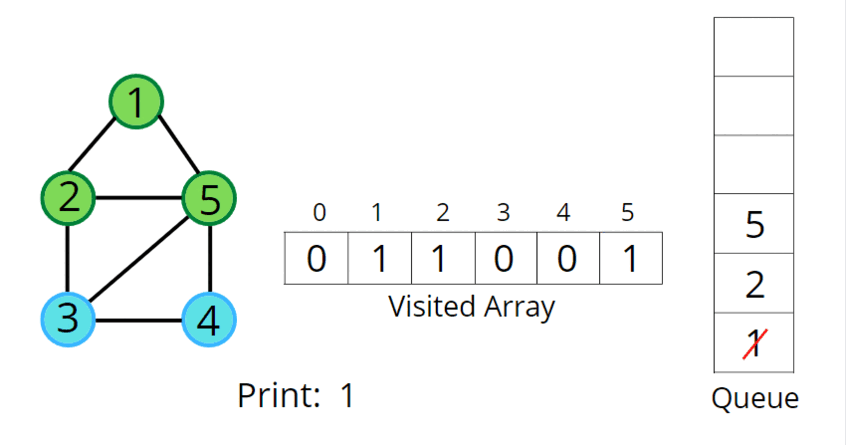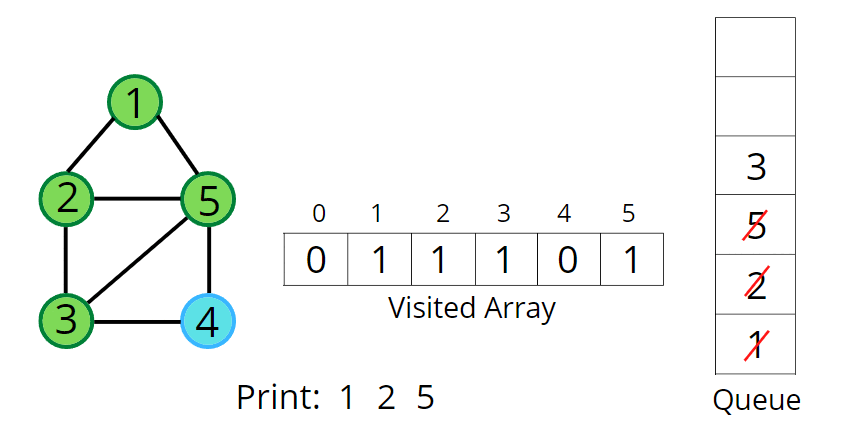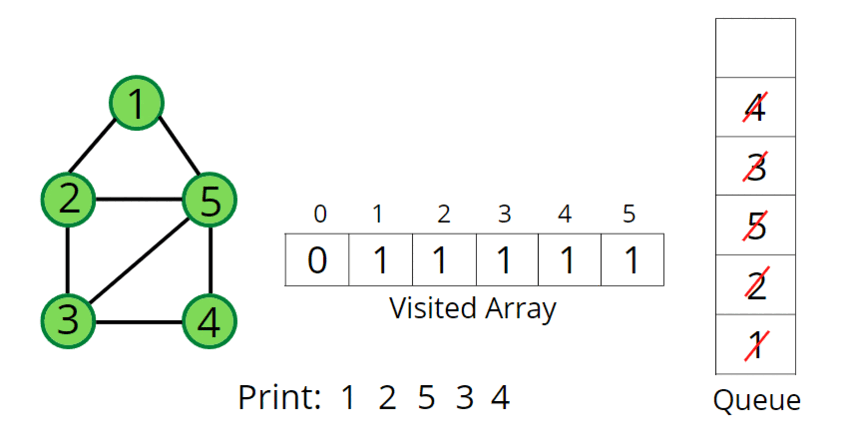
- BFS 인접행렬 구현
/*
정점수
간선수
탐색시작노드
간선수만큼 연결정보
5
5
1
1 2
1 5
2 3
2 4
3 4
출력: 1 2 5 3 4
*/
package graph;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BFS_인접행렬탐색 {
static int[][] arr;
static boolean[] isSelected;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int V;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
arr = new int[V + 1][V + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
arr[u][v] = arr[v][u] = 1;
}
isSelected = new boolean[V + 1];
// 1. Queue 만들기
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 2. q에 start node 넣기
q.offer(start);
// 3. 방문 체크
isSelected[start] = true;
// 4. q에서 데이터 꺼내 처리
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int curV = q.poll();
// 5. 하고 싶은 일 수행
sb.append(curV).append(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
if(!isSelected[i] && arr[curV][i] != 0) {
// 6. 갈 수 있는 새 정점을 q에 넣기
q.offer(i);
isSelected[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
}- BFS 인접리스트 구현
/*
정점수
간선수
탐색시작노드
간선수만큼 연결정보
5
5
1
1 2
1 5
2 3
2 4
3 4
출력: 1 2 5 3 4
*/
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BFS_인접리스트탐색 {
static List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] isSelected;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int V;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= V; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
list.get(u).add(v);
list.get(v).add(u);
}
isSelected = new boolean[V + 1];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
isSelected[start] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int curV = q.poll();
sb.append(curV).append(" ");
for(int i : list.get(curV)) {
if(!isSelected[i]) {
q.offer(i);
isSelected[i] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
}
👩🏻💻 문제 풀어보기: 백준_DFS와 BSF_1260
package graph;
import java.util.*;
public class 백준_DFS와BFS_1260 {
static List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] isSelected;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
list.get(u).add(v);
list.get(v).add(u);
}
// 각 정점의 연결 리스트를 정렬 (오름차순 방문을 위함)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Collections.sort(list.get(i));
}
isSelected = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(start);
sb.append("\n");
isSelected = new boolean[n + 1];
bfs(start);
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
static void dfs(int cur) {
isSelected[cur] = true;
sb.append(cur).append(" ");
for(int i : list.get(cur)) { // 갈 수 있는 곳들만 뽑음
if(!isSelected[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
}
static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
isSelected[start] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int curV = q.poll();
sb.append(curV).append(" ");
for(int i : list.get(curV)) {
if(!isSelected[i]) {
q.offer(i);
isSelected[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}728x90
반응형
'LG 유플러스 유레카 SW > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [#21] MST(최소신장트리) + 다익스트라 알고리즘 (1) | 2025.02.24 |
|---|---|
| [#20] 알고리즘 - 최단 경로 (0) | 2025.02.21 |
| [#18] 비선형 자료구조 - 트리 (0) | 2025.02.19 |
| [#17] 순열 & 조합 & 부분집합 (0) | 2025.02.18 |
| [#16] 알고리즘 - 정렬 (0) | 2025.02.17 |